Classification of Grasses - continued
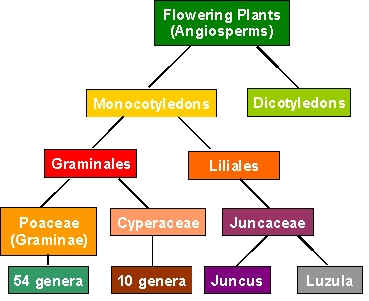 (The numbers of genera given are for Britain only) |
The Flowering Plants are divided into two groups, the Monocotyledons
and the Dicotyledons. Grasses, sedges and rushes all belong to the Subclass Monocotyledons. They can easily be distinguished from the Dicotyledons in that they have:
The grasses and the sedges belong to the Order Graminales (a further subdivision of the Monocotyledons). |
| Features of the Order Graminales
Grasses are in the Family Poaceae, (also known as Gramineae), and Sedges are in the Family Cyperaceae. The main differences are:
The Rushes are in the order Liliales and have many similar features to Lily flowers, except that the petals and sepals are small, brown and scale-like and are called tepals. (They are called tepals collectively, because the sepals and petals look exactly the same and are indistinguishable from each other.) Rushes belong to the Family Juncaceae. The main features of this family are:
There are 2 genera of rushes in Britain, (in contrast to the 54 genera of grasses).
Continue to |




