The Woodland Education Centre
Heathland Project Report Report Introduction Contents Summary
The Effects of Management - Brushcutting
 a) General
a) General
ii) Tree Seedlings
The growth of trees on heathland sites is one of the major obstacles to maintaining heath vegetation and associated fauna. Tree seedlings, particularly Silver Birch and Pine, readily colonize heath areas. Unless their growth is checked by fire, cutting or grazing, they rapidly grow tall, shading out the underlying heath vegetation, which is unable to compete. Succession from heathland to woodland is the natural consequence.
Silver Birch (Betula pendula) and Cherry (Prunus sp.) are the major tree species currently colonizing the project site. Sycamore (Acer pseudoplanatus) seedlings were common on the site in 1996, but have disappeared over the past two years. Other tree species colonizing the area include Holly (Ilex aquifolium), Rowan (Sorbus aucuparia), Oak (Quercus sp.), Ash (Fraxinus excelsior), Willow (Salix spp.) and Rhododendron (Rhododendron ponticum). Rhododendron is now present in sections 1,5 and 9.
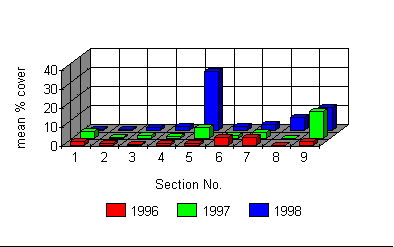
Distribution of Silver Birch. 1996 - 1998
mean % cover
Silver Birch is distributed over the whole site (Figures above and below), but is now most abundant in sections 5 and 9. Neither of these sections are cut, allowing the Silver Birch to grow freely. Section 5 is the control section and will not be touched. However, section 9 has hand weeding as part of its management regime, and this option may be exercised in future to control the Birch in this area.